Facts you should know about car engines
FACTS ABOUT CAR ENGINES YOU SOULD KNOW
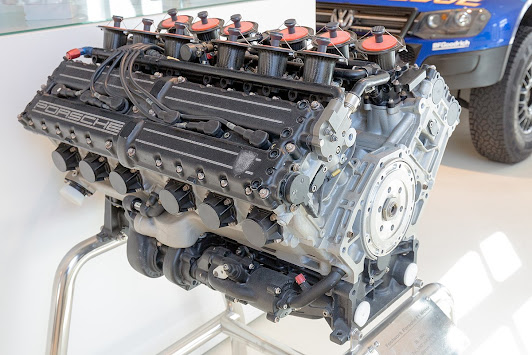
Modern cars of nowadays are been powered by four-stroke, internal combustion gasoline engines. this engine has been refined, as technology has advanced for the past century. while even basic car engines is a complex machine, the principle behind it's operation is easy to handle.
The four-stroke cycle
Problems
Car engines experience a variety of problems. Some of these can be repaired simply, and others may make the engine permanently in-operate-able. Using gasoline with a low octane(colourless flammable hydrocarbon of the alkane series present in petroleum spirit) rating can result in engine knocking, which is actually a premature combustion in one of the cylinders. A cracked engine block is one of the most serious problems an engine can have. Blown head gaskets are more common, and can occur when an engine overheats or the gasket wears down. A broken connecting rod or faulty spark plug can leave an engine with one or more non-functional cylinders, robbing it of power.
Maintenance
While most car engines will eventually require major repair, a basic maintenance schedule should be followed to ensure that the engine lasts as long as possible and operates safely and efficiently. Regular oil changes are a must, as new oil will keep the engine lubricated and running smoothly. In addition, keeping an adequate level of engine coolant in the car will keep an engine from overheating. Occasionally spark plugs may need to be changed. The engine air filter, which cleanses the air that is blended with fuel prior to combustion, is another item that should be replaced as needed.
Other Type of Engines
Besides the standard, gasoline-powered internal combustion engine, other types of engines are used in some cars. While the vast majority of engines are reciprocating piston engines as described here, rotary engines operate on similar principles but use a spinning rotor in place of a set of pistons to create compression. Diesel engines are similar to gasoline engines but are designed to burn diesel, which is ignited with hot air instead of sparks. Cars that use alternative fuels, such as hydrogen or electricity, are also becoming more common in our present world today.
Here are some Symptoms of a Bad Oxygen Sensor
A bad oxygen sensor can impact an engine's performance negatively in plenty of ways. Because of the very important role an oxygen sensor plays in the maintenance of good and clean air and fuel levels in a running engine, any faulty or spoilt oxygen sensor function can create several engine symptoms that are beyond repair.
Poor Gas Mileage
Oxygen sensors play an important role in adjusting a vehicle engine's air, the combination of gas and air(combustion) an engine burns to produce power. A faulty oxygen sensor may allow too much fuel to be added to the air, resulting in poor gas mileage.
Emissions of the vehicle increases
Oxygen sensors monitor and adjust an engine's fuel mixture to ensure proper combustion, vehicle emissions and performance. A bad oxygen sensor can result in poor fuel mixtures or lean or rich fuel-injection delivery, all of which can cause inefficient engine combustion and increase the vehicle emissions.
Rough Engine Idle
Proper engine combustion is crucial for maximizing engine performance. A bad oxygen sensor can cause a car's engine to idle in a rough manner. This is caused by the less-than-optimum engine combustion firings that result in poor engine performance.
Engine Missing
If a bad oxygen sensor causes an engine's air to become too lean or restricted, the explosions within an engine combustion will be altered. Normally, a fuel mixture that is too lean (too much air, not enough fuel) will cause an engine to miss, or misfire, especially when an engine is idling.
Engine Hesitation
Engine hesitation is very similar to engine missing. However, engine hesitation is experienced only during acceleration, while an engine miss can be experienced both during engine acceleration and idle. A bad oxygen sensor may misinterpret an engine's fuel mixture or fuel requirements and cause too little or too much air or fuel to enter an engine's cylinders, especially during acceleration. This can cause an engine to hesitate, or stumble.
SIGNS & SYMPTOMS OF A DAMAGED FUEL FILTER
A fuel filter is necessary to prevent dirt and other particles from damaging a vehicle's fuel delivery system, a condition that severely disrupts engine performance. Fuel filters can themselves become clogged, and when that happens, engine power and performance are negatively affected.
No-Start Condition
If a fuel filter is totally blocked or clogged to the point of blocking fuel flow to a vehicle's engine, the vehicle will not start. Fuel combined with air is what is ignited inside a vehicle's engine to get it started.
Hard-Start Condition
A partially blocked or clogged fuel filter will often result in a vehicle that is hard to start. Adequate fuel flow to a vehicle's engine is needed to produce engine starting. A reduced or restricted fuel flow to a vehicle's engine will hinder normal starting.
Frequent Engine Stalling
For a vehicle's engine to run efficiently and adequately, a constant flow of fuel needs to reach the engine. Any disruption of this fuel flow, which is what happens when a fuel filter is clogged, can cause an engine to frequently stall.
Engine Hesitation
Engine hesitation is a common symptom of a clogged fuel filter. By causing an abnormal fuel flow to a vehicle's engine, a condition that results in abnormal engine combustion and reduced engine power, a clogged fuel filter can cause an engine to hesitate or stumble during acceleration.
Erratic Engine Performance
A clogged fuel filter often results in erratic engine performance by causing an abnormal or alternating pattern of fuel flow into a vehicle's engine. Under heavy acceleration or at high engine speeds, fuel pressure may be sufficient to allow adequate fuel flow past a partially clogged filter, which results inadequate engine performance. When engine speed is reduced, fuel flow may be restricted to the point of causing reduced engine power and performance.
HERE IS A VIDEO ON HOW THE ENGINE WORKS


Comments
Post a Comment